INTERVIEWS
Introduction
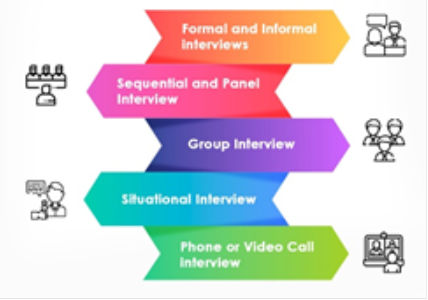
Interviews [Figure 1.0] are an important part of the
selection process because they can help HR professionals meet a variety of
candidates and determine which one is right for their company's needs (Einhorn,1981). Additionally, interviews can help
you identify prospective employees who align with your company's goals and
culture (Munro, 2016).
Figure 1.0 Types of Interviews
Interviewer’s Interviewing Skills
Munro,
J. (2016) has stated interviewer’s
main job in the interview is active listen. A
reasonable benchmark as the interviewer is to aim for the 80/20 rule: 80% listening and 20% talking.
Actively listen skill may discover motivations, attitudes and values that
didn’t show up on their paper qualifications. During the interview, interviewer
pay attention to candidate’s answers and the non-verbal cues [Figure 2.0] you
use while answering questions (Allyn, & Bacon, 2009).
Figure 2.0 Active Listening Skills
Source:
(Anderson, R. & Killenberg, G. 2009)
Interviewing Questions
The interviewer, poses a series of questions
about the candidate's job experience and expertise (Einhorn, 1981). Main three
forms of Interview questions are competence
based questions, hypothetical questions, and personal awareness questions.
These questions are designed to explore what the candidate has done, and the
skills that they have previously demonstrated (Anderson, & Killenberg,
2009). Other than that these questions
are designed to explore how candidates will deal with the problems that are
likely to face them in this post. Personal awareness questions are designed to
explore the fit between the candidate’s needs and what the job or organization
can offer (Richard, 2014).
Guide
Line for Conducting Effective Interview
Munro,
(2016) states following steps to conduct effective interview,
•
Interviewer should always plan in advance
the venue and time.
•
Should behave friendly with the
respondent.
•
Should have the ability to mobilize the
respondent to answer freely and frankly.
•
Questions should be well framed and avoid
complex questions.
•
Should have an unbiased approach.
•
Should not indulge in any argument.
•
Should show gratitude for the respondent.
References
·
Anderson, R. & Killenberg, G. (2009), Interviewing,
speaking, listening, and learning for professional life. New York: Oxford
University Press. Pp 124-8.
·
Einhorn, L. (1981), An inner view of the job
interview: An investigation of successful communicative behaviors.
Communication Education,217–228.
·
Gouran, D. (2014), Mastering communication (2nd
ed.). London: Routledge, pp 18-27.
·
Allyn, R. & Bacon. L. (2009).A simulated job
interview setting. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 33, 1–16.
·
Munro, J. (2016), A Handbook of Employment
Interviewing, Macdonald and Evans, London, pp 108-111.
·
Richard, S. (2014), Interviewing: More than a Gut Feeling, Provant Media
Publishing, Urbandale, Iowa, pp.8-12.

Interviews are used to obtain detailed information about the experiences of participants by interpreting them. Biases should be avoided by interviewers. For example, when confronted with a subject in which interviewer feel connected and close to it, interviewer must remember that their duty is to listen to and understand the participants' points of view while remaining objective. Although there are various methods for qualitative data collection, such as text or document reviews, diaries, and participant observation, interviews are the most commonly used techniques for primary qualitative data collection because that provide participants with a natural and comfortable environment (Taherdoost, 2022).
ReplyDeleteVirosha, there is a valid point in your comment. According to Ali, B, J. (2021), qualitative factors are outcomes that you cannot quantify with hard data. Although numerical data is not used to measure them, qualitative factors are still incredibly influential because they represent the way the public perceives a business and its operations and how that perception can affect the bottom line. Interviewer should consider qualitative factors as part of his or her analysis of a decision (Ali, B. J., & Anwar, G. 2021). Depending on the interviewer and the level of job
Deleteinvolved, qualitative factors can be the deciding point.
Hi, when studying about the interviews I just come across the Internal Recruitment hope this is helps to you,
ReplyDeleteInternal Recruitment is:
This is for those people who are already working in the organization; the HR people
publish the circular on notice board and online portal to invite the deserving employees
to participate in the interview via they can also upgrade their position level and avail
their career growth. In this case, employees refer their resume personally and
sometimes by their internal communication portal. This process may not be followed in
all companies and organizations, for example in the study (Sintheya Rahman 2011).
Some of the advantages of internal hiring have been mentioned. We review what each
of Stonner, Freeman and Gilbert (2000) identified three advantages of an organization
policy to recruit from within. First, individuals recruited from within are already familiar
with the organization and its members, and this knowledge increases the likelihood that
they will succeed. Secondly, a promotion from within policy fosters loyalty and inspires
greater effort among organization members. Finally, it is usually less expensive to recruit
or promote from within than to hire from outside the organization. Certain
disadvantages to internal recruitment were also recognized. It limits the pool of
available talent. In addition, it reduces the chance that fresh view points will enter the
organization, and it may encourage complacency among employees who assume
seniority ensures promotion.
Because internal sources are often not sufficient to supply a suitable pool of applicants , most organisations make use of external sources. There are many such sources , including employ referrals, employment agencies, 'walk-ins' , and going direct to educational establishments.(Bach,2009)
ReplyDeleteAlso sometimes interviews can have a disproportionate amount of influence on the hiring decision. The applicant who performs poorly in the job interview is likely to be eliminated from the applicant pool regardless of experience, test scores, or letters of recommendation (Robbins & Judge, 2011).
ReplyDeleteIsuri, you can demonstrate an ability to influence by listening closely to those who disagree with your position. When you acknowledge someone else's viewpoint, you establish rapport.This can encourage your opponent to give you the same courtesy and listen to your viewpoint (Ali, B. J., & Anwar, G. (2021).
Delete